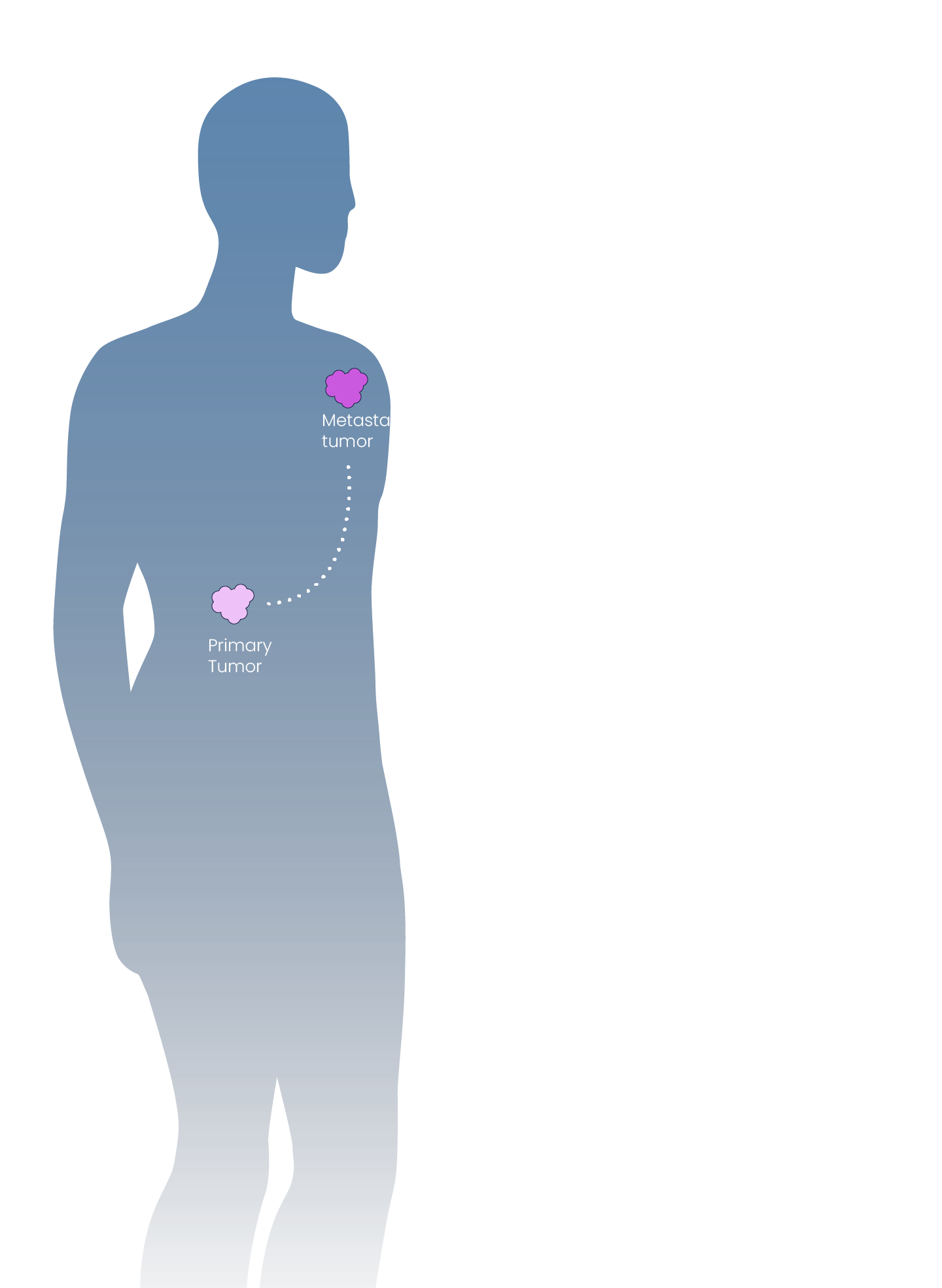
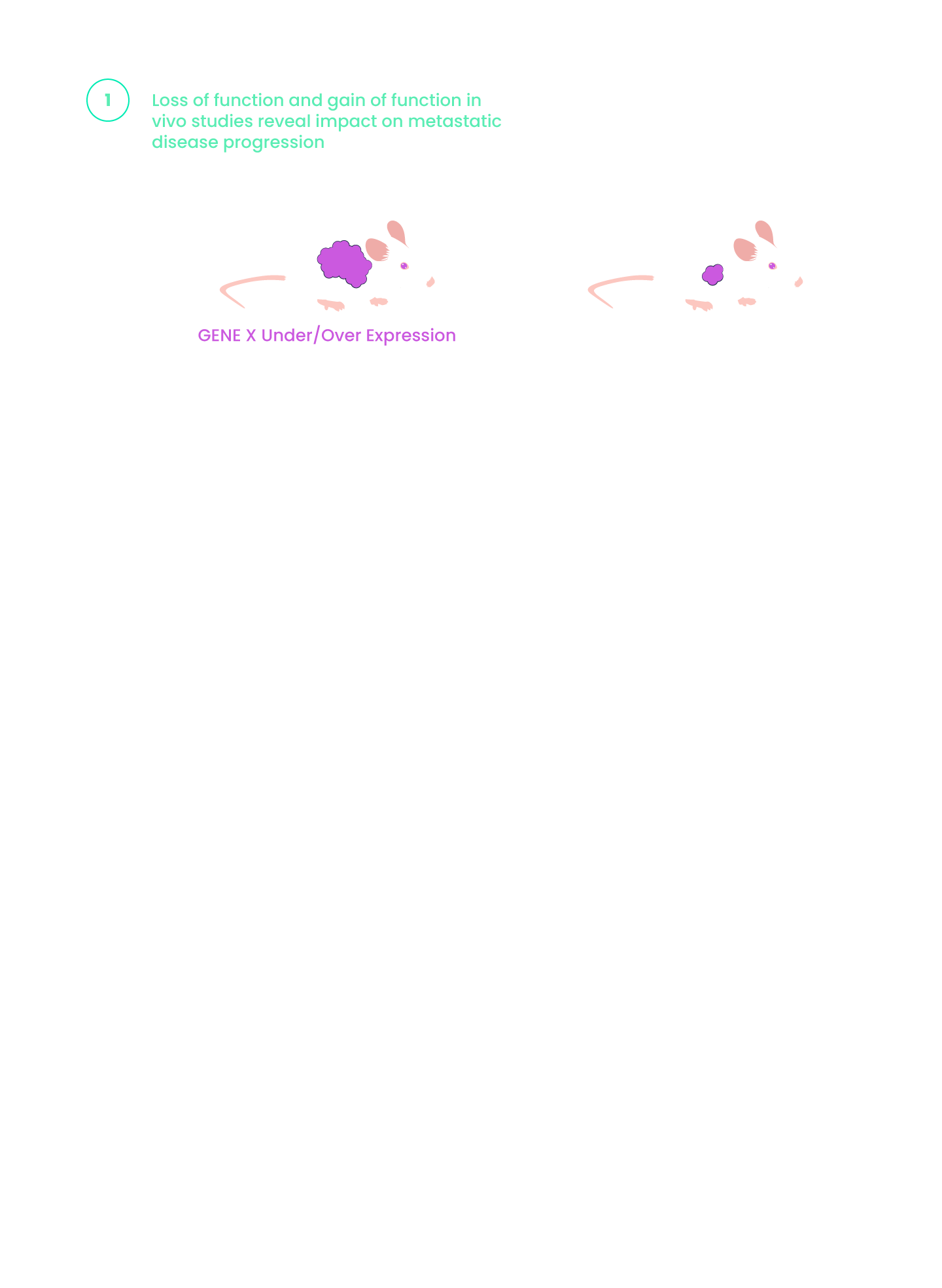
Inspirna’s novel target discovery platform, miRNA-DRIVEr, reveals new cancer drivers through microRNA profiling.
Inspirna has developed the unique expertise to discover novel and actionable cancer drivers that affect large patient populations. We conduct comprehensive studies including genomic, transciptomic, proteomic and metabolomic approaches for the identification and validation of our targets as well as the characterization of the underlying biology. The team has extensive expertise across all areas of drug development to move programs quickly from lab-to-clinic. Our approach has generated extensive scientific and preclinical data, which have led to multiple publications in high profile journals.
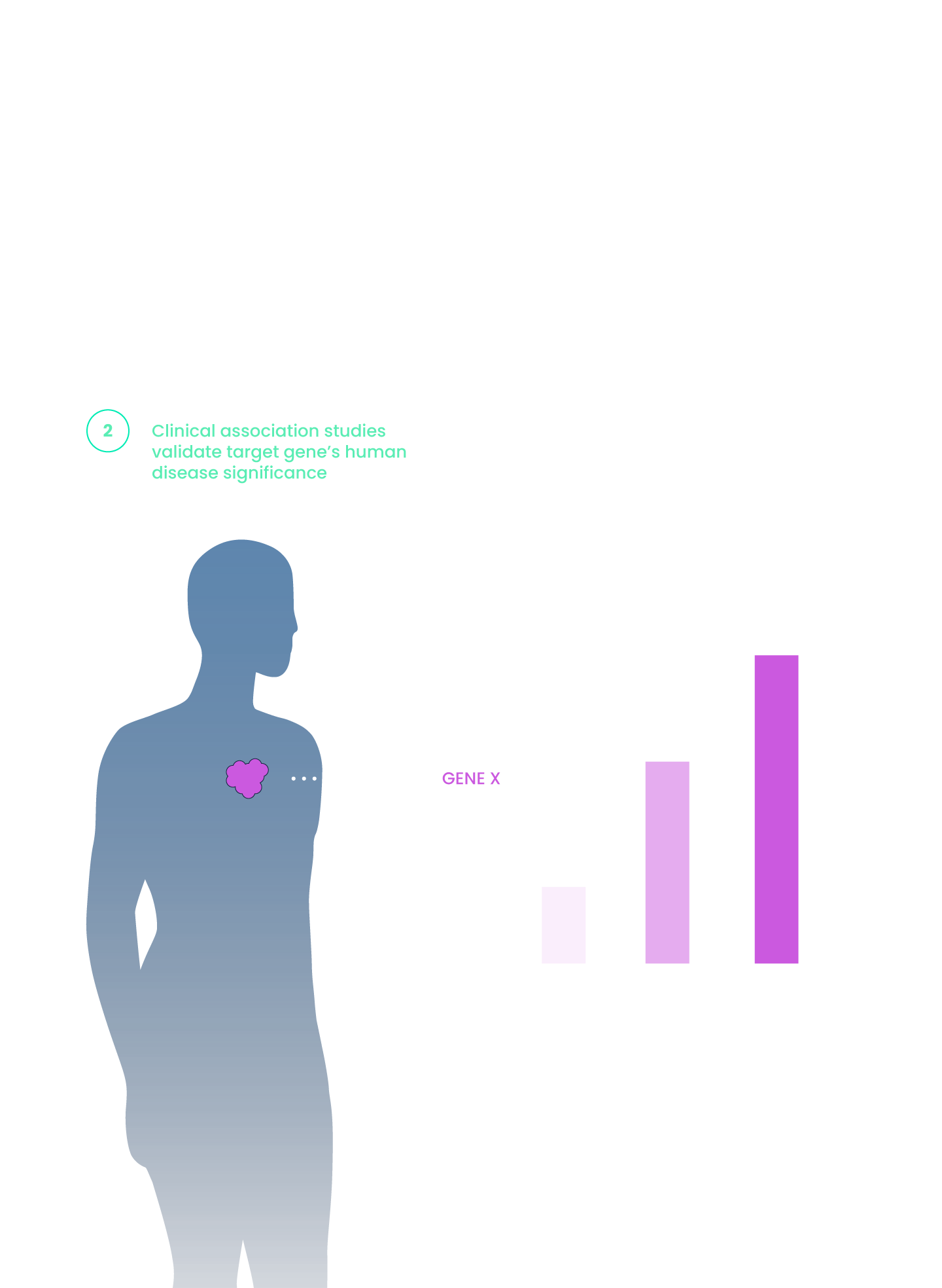
Our proprietary and clinically-validated miRNA-DRIVEr platform, coupled with our expertise in miRNA mapping, allows us to reveal new cancer drivers and actionable targets of miRNA dysregulation.
miRNA-DRIVEr = miRNA Dysregulated Drug Target In Vivo Elucidation
Why target miRNA regulated pathways?
Micro RNAs (miRNAs)* have important biological functions:
- Regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level;
- Modulate cell growth and differentiation;
- Regulate pathways and networks via coordinated activities;
- Act co-operatively with other miRNAs and with transcription factors, which are frequent targets of miRNAs.
miRNA dysregulation is a frequent contributor to cancer growth and progression.
- Overexpression or depletion of distinct sets of miRNAs is frequently found in cancer.
- Delineating miRNA functional effects requires elucidation of their upstream regulators and downstream targets.
*short, endogenous noncoding RNAs 19–22 nucleotides long
Our miRNA-DRIVEr platform reveals actionable miRNA-dysregulated cancer targets
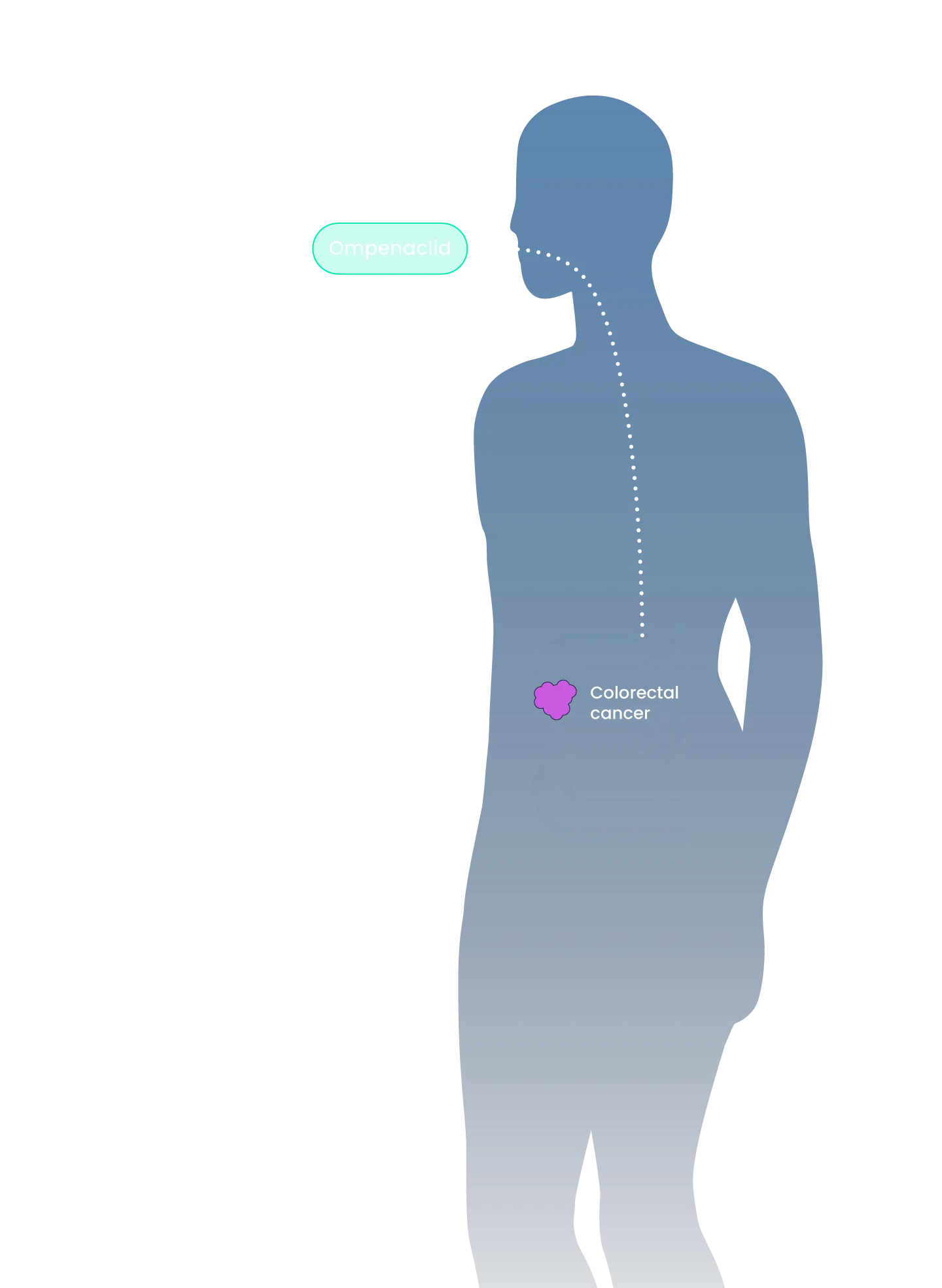
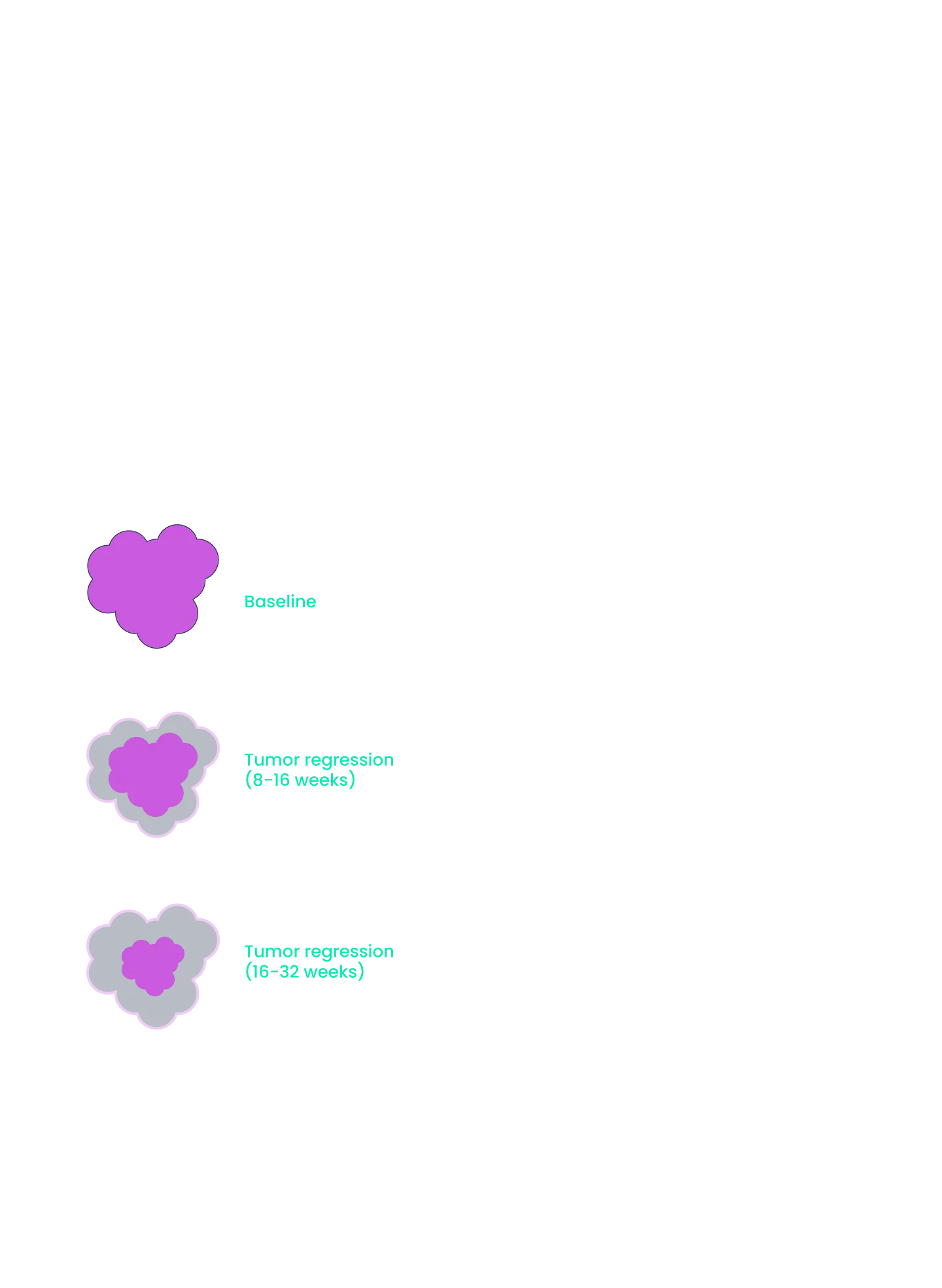
We are dedicated to stopping metastatic progression and providing long-term survival benefits for patients by providing more practical treatment options that prolong survival without decreasing quality of life. Our innovative medicines possess improved dosing schedules and safety profiles that will become seamless and simple additions to the existing standard of care (i.e., oral BID) to treat indications with large patient populations and high unmet need.